JsonLogic extensions
JsonLogic is a library for processing rules written in JSON. A JsonLogic rule is structured as follows: { "operator" : ["values" ... ] }. For example, { "cat" : ["I love", "pie"] } results in "I love pie".
Sensible supports both built-in and extended JsonLogic operators so that you can transform and validate extracted document data.
Documentation
-
For a Sensible-specific tutorial, see The opinionated guide to JsonLogic for transforming document data.
-
For information about the base built-in JsonLogic operators, see the documentation.
-
Sensible supports extended operations available in the Json Logic Engine library. For more information, see the documentation. For example, this engine includes the following extended operations:
- Array operations:
"length","get". - Miscellaneous operations:
"preserve","keys". - Higher order operations:
"every","eachKey"
- Array operations:
Syntax tips
- Use dot notation to access properties of an object (by name) or items in an array (by index), for example,
test_table.columns.3.valuesto access the 4th column in a table. - Double escape dots in field IDs. For example,
"delivery\\.zip\\.code.value"to reference87112in the field{"delivery.zip.code":{"value":87112}}. - Use traversal notation to access data in hierarchies. For example, in a section, use
"../"to access fields in the parent object. - To evaluate the current context, use
"var":"". - The
"var"operator returns null if you attempt to reference a field that Sensible can't find in theparsed_document. - Math that include a null return null. For example,
5 + null field = null. If you instead want5 + null field = 5, then implement logic to replace nulls with zeros. For an example, see Example 1.
Sensible-specific operations
Sensible extends JsonLogic with custom operations. The following table lists these operations and where they're supported:
| Operation | Validations | Custom computation methods | Postprocessor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Date Shift | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Exists | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Flatten | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Group | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Join | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Let | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Log | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Map Object | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Match | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Merge Objects | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Object | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Omit fields | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Pick Fields | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Replace | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Round | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Slice | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Sort By | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Stateful Map | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
See the following sections for more information.
Date Shift
Use this operation to add or subtract days, months, or years to a date.
Takes as input:
-
a date. Can be any date string for which the JavaScript
Dateobjects 'getTime()function can return a number. For example, can be an ISO 8601-formatted Sensible date type, orFebruary 27, 2024or12-31-2022. -
a number
-
a unit (
"days","months", or"years")
Returns an ISO 8601-formatted date-time string that's the result of adding the number of units to the date. Use negative numbers to calculate prior dates.
For example:
{
"fields": [
{
"id": "add_years",
"method": {
"id": "customComputation",
"jsonLogic": {
"date_shift": [
"2024-01-02",
3,
"years"
]
}
}
},
]
}returns:
{
"add_years": {
"value": "2027-01-02T00:00:00.000Z",
"type": "string"
}
}Exists
Returns a boolean to indicate if the specified value exists. Returns false if the value is null or undefined.
{
"exists": JsonLogic
}Most commonly used with the JsonLogic var operation to test a field's output.
Accepts as input:
- a single value, e.g.,
{ "exists": { "var": "some_field" } }) - an array, in which case it checks the first item only, e.g.,
{ "exists": [{ "var": "some_field" },...,] }
Examples
Flatten
Takes as input an array that can contain any depth of nested arrays, and returns a single-level array populated with the same values.
Examples
The following example shows how to flatten a nested array. It also shows how Sensible transforms the JsonLogic output into the fields schema when you use Flatten inside the Custom Computation method.
{
"fields": [],
"postprocessor": {
/* returns a flat array, i.e. [1,2,3,4,5,6,7] */
"type": "jsonLogic",
"rule": {
"flatten": [
[
1,
[
2,
3
],
[
4,
[
5,
6,
7
]
]
]
]
}
},
/* since the output must be a field or fields,
custom computation wraps the returned output
in value/type syntax, i.e., `{ "value": 1, "type": "number" },
{ "value": 2, "type": "number" }, ... ]` */
"computed_fields": [
{
"id": "flatten_in_custom_comp",
"method": {
"id": "customComputation",
"jsonLogic": {
"flatten": [
[
1,
[
2,
3
],
[
4,
[
5,
6,
7
]
]
]
]
}
}
},
],
}returns the following:
// in postprocessorOutput
[
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7
]
// in parsed_document
{
"flatten_in_custom_comp": [
{
"value": 1,
"type": "number"
},
{
"value": 2,
"type": "number"
},
{
"value": 3,
"type": "number"
},
{
"value": 4,
"type": "number"
},
{
"value": 5,
"type": "number"
},
{
"value": 6,
"type": "number"
},
{
"value": 7,
"type": "number"
}
]
}Group
Groups an array of objects by the specified key and returns computed fields for each group:
"group":
[
[ /* array_of_objects_to_group */ ],
"key_to_group_by",
[[/* field_to_return */ ], [/* field_to_return */ ] ... ] /* specify each field_to_return with syntax ["key", JsonLogic] */
]For example, the following code groups an array of clothes objects by their apparel type:
{
/* groups a list of items by a property (`apparel_type`),
and for each group, returns computed fields
*/
"fields": [],
"postprocessor": {
"type": "jsonLogic",
"rule": {
/* */
"group": [
{
/*
The array of objects to group.
In practice, you often input an
array with `{"var":"field_key"}` syntax.
This example uses `preserve` to input an
array constant
as literal JSON rather than JsonLogic
*/
"preserve": [
{
"apparel_type": "shirt",
"color": "yellow"
},
{
"apparel_type": "dress",
"color": "green"
},
{
"apparel_type": "shirt",
"color": "red"
}
]
},
/* group by the `apparel_type` key */
"apparel_type",
/* for each group, return the following fields:
- group key
- count of items in group
- array of colors of items in group */
[
/* return a field with the value of the group key */
[
"group_key",
{
"var": "key"
}
],
/* return a field with the group item count */
[
"count_of_items_in_group",
{
"length": {
"var": "values"
}
}
],
/* return a field with the colors of items in the group*/
[
"colors_in_group",
{
"map": [
{
"var": "values"
},
{
"var": "color"
}
]
}
]
]
]
}
}
}The preceding code sample returns the following output:
[
{
"group_key": "shirt",
"count_of_items_in_group": 2,
"colors_in_group": [
"yellow",
"red"
]
},
{
"group_key": "dress",
"count_of_items_in_group": 1,
"colors_in_group": [
"green"
]
}
]Join
Performs a left join on two arrays using a common key, and returns a new array containing elements of both.
"join": [
/* 1st arg */
[
[/* input array A */ ],
{ /* key to join arrays by */ },
/* name for this input array. if unprovided,
defaults to tableA */
"array_A"
],
/* 2nd arg */
[
[/* input array B */ ],
{ /* key to join array by */ },
/* name for this input array. if unprovided,
defaults to tableB */
"array_B"
],
/* 3rd arg */
{
/* operation to output a new array using the input arrays,
for example, eachKey operation.
output array is same length as array A
if an item in array A corresponds to multiple items in array B,
operation takes an arbitrary corresponding item from array B */
}
]For example, the following code joins a customers array and an orders array by the customer ID, then creates a new array using elements from both arrays.
{
"fields": [],
"postprocessor": {
"type": "jsonLogic",
"rule": {
"join": [
[
/* 1st input array
In practice, you often input an
array with `{"var":"field_key"}` syntax.
This example uses `preserve` to input an
array constant
as literal JSON rather than JsonLogic*/
{
"preserve": [
{
"order_description": "office chairs",
"customer_id": "c1",
"amount": 50
},
{
"order_description": "ink cartridges",
"customer_id": "c2",
"amount": 75
},
{
"order_description": "whiteboards",
"customer_id": "c3",
"amount": 30
},
{
"order_description": "desks",
"customer_id": "c1",
"amount": 40
}
]
},
/* key to join arrays by */
{ "var": "customer_id" },
/* name for this input array. if unprovided, defaults to tableA */
"orders_array"
],
[
/* 2nd input array */
{
"preserve": [
{ "id": "c1", "first_name": "Sally", "last_name": "Smith" },
{ "id": "c2", "first_name": "Ahmed", "last_name": "Aamer" }
]
},
/* key to join array by */
{ "var": "id" },
/* name for this input array. if unprovided, defaults to tableB */
"customers_array"
],
{
/* create a new joined array, where each array element contains parameter values from array 1 and array 2*/
"eachKey": {
"order_descrpt": { "var": "orders_array.order_description" },
"amnt": { "var": "orders_array.amount" },
"name": {
/* if first_name is absent for a customer_id, output "Unknown" instead of default (null) */
"if": [
{ "var": "customers_array" },
{ "var": "customers_array.first_name" },
"Unknown"
]
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
returns
[
{
"order_descrpt": "office chairs",
"amnt": 50,
"name": "Sally"
},
{
"order_descrpt": "ink cartridges",
"amnt": 75,
"name": "Ahmed"
},
{
"order_descrpt": "whiteboards",
"amnt": 30,
"name": "Unknown"
},
{
"order_descrpt": "desks",
"amnt": 40,
"name": "Sally"
}
]Let
Use this operator to declare named variables scoped to the Let operator. This operator addresses JsonLogic's lack of built-in support for named variable declaration.
{
"let": [
{ /* 1st arg: initialize named variables using key/value pair syntax */ },
{ /* 2nd arg: operate on the named variables. Sensible evaluates variables in order */ }
]
}Example
{
"fields": [],
"postprocessor": {
"type": "jsonLogic",
"rule": {
"let": [
{
/* declare values with key:value pair syntax */
"a": 5,
"b": 3,
/* c is sum of a + b (8) */
"c": {
"+": [
{
"var": "a"
},
{
"var": "b"
}
]
}
},
/* operate on named values (5 * 8) */
{
"*": [
{
"var": "a"
},
{
"var": "c"
}
]
}
]
}
}
}This returns:
/* postprocessor output */
40Log
Note that this operation replaces the native JsonLogic operation.
Takes as input an array, where the first argument is the log message and the second is a JsonLogic expression you want to evaluate.
{
"log": [
"log message",
JsonLogic
]
}The log operation doesn't modify extracted document data. It returns its results as part of the extraction errors. Sensible passes the data wrapped in a log operation to whatever other operations surround it as if "log" were not there. For example { "*": [{ "log": ["first multiplication item", { "+": [1, 2] }], 4}] } returns 12 and a log in the extraction errors with the fields "message": "first multiplication item" and "result": 3.
To view the results of the Log operation, see the errors array of the API extraction response, or see the Errors tab of the SenseML editor's output pane.
Examples
See Advanced: Transform sections data.
Map Object
For an object containing key-value pairs, iterates over the object and operates on each key and each value:
"mapObject": [
{ /* key_value_pairs_to_map */},
[
{ /* JsonLogic_for_keys */ },
{ /* JsonLogic_for_values */ }
]
]Example
The following example shows extracting fields, then modifying the key and the value for each field.
Config
{
"fields": [
{
"method": {
"id": "queryGroup",
"searchBySummarization": "page",
"queries": [
{
/* extract fields */
"id": "lime pies",
"description": "number of lime pies",
"type": "number"
},
{
"id": "apple pies",
"description": "number of apple pies",
"type": "number"
},
]
}
}
],
"postprocessor": {
"type": "jsonLogic",
"rule": {
"mapObject": [
{
/* The object to map. In this case, the current context,
i.e. the extracted fields
*/
"var": ""
},
[
{
/* operation to perform on each field's key */
"cat": [
/* prefix each key with its meal category */
"DESSERT_",
{
"var": "key"
},
]
},
/* operation to perform on each field's value */
{
/* multiply the value by 4 */
"*": [
{
/* since each field's value is an object,
access nested value with value.value */
"var": "value.value"
},
4
]
}
]
]
}
}
}Example document
The following image shows the example document used with this example config:

| Example document | Download link |
|---|
Output
// FIELD OUTPUT
{
"lime pies": {
"source": "3",
"value": 3,
"type": "number",
"confidenceSignal": "confident_answer"
},
"apple pies": {
"source": "5",
"value": 5,
"type": "number",
"confidenceSignal": "confident_answer"
}
}
//POSTPROCESSOR OUTPUT
[
[
"DESSERT_lime pies",
12
],
[
"DESSERT_apple pies",
20
]
]
Match
Returns a boolean to indicate if the specified regular expression matches.
{
"match": [
{ /* JsonLogic that evaluates to the text in which to find the match */ },
" /* JavaScript-flavored regular expression */ ",
" /* optional: case-insensitive flag (i) */ "
]
}Double escape special regex characters since the regex is in a JSON object. For example, use \\s, not \s , to represent a whitespace character.
Examples
{
"fields": [
{
"id": "customer_id",
"method": {
"id": "constant",
"value": "ID1234",
},
},
{
// check that customer ID is formatted as "ID" + 4 digits (case-insensitive)
"id": "correct_id_format",
"method": {
"id": "customComputation",
"jsonLogic": {
"match": [{ "var": "customer_id.value" }, "^id\\d{4}$", "i"],
},
},
},
],
}
This example returns:
{
"customer_id": {
"value": "ID1234",
"type": "string"
},
"correct_id_format": {
"value": true,
"type": "boolean"
}
}Merge objects
For an array of objects, returns a single object containing all the fields from each object.
Edge cases:
- If passed an empty array, it returns an empty object
- If passed an array containing a value that is
nullorundefined, ignores that value but still returns an object based on object values that were passed - If passed an array containing a value that is not an object,
null, orundefined, throws an error - If passed multiple fields that use the same key, uses the last value that is passed for that key.
For example, the following simple code:
{
/* Note: this example works in a Postprocessor object
it doesn't work in a Custom Computation method because of output schema constraints */
"merge_objects": [
{ "eachKey": { "field1": "hello" } },
{ "eachKey": { "field2": "world" } }
]
}
returns the output:
{
"field1": "hello",
"field2": "world"
}Examples
See the Stateful Map operation for a full example.
Object
Returns a JSON object that is an array of key/value pairs. You can nest object operations to build complex custom objects. This operation is an alternative to the "eachKey" operation. Use the Object operation when the keys in the object you intend to build can vary depending on other operations:
{
/* Sensible recommends the Ojbect operation as an alternative to the "eachKey" operation if you don't know the keys in the object before building it */
"object":
[
/* where the JsonLogic operation returns `[["string", value] ...]`, e.g., map */
JsonLogic
]
}Omit fields
Creates a new object that includes all the fields from a source object except those specified. Takes an array of two items:
- an object to get fields from
- an array of field IDs to omit
{
"omit_fields": [
sourceObject,
["field_id_1", "field_id_2", "field_id_3"]
]
}Edge cases:
- The Omit Fields operator returns an empty object if the source object is empty, null, or undefined
- The Omit Fields operator returns the source object if it can't find the specified fields to omit.
Examples
Example 1
As a simplified example, given the following extracted fields:
{
"field_morning": "good morning",
"field_afternoon": "good afternoon",
"field_evening": "good evening"
}if you apply the rule:
{
"omit_fields": [
// `"var": ""` returns the current context, in this case, the preceding extracted fields
{ "var": "" },
// the IDs of the fields to be omitted
["field_morning"]
]
}the rule outputs:
{
"field_afternoon": "good afternoon",
"field_evening": "good evening"
}Example 2
The following example shows removing extracted IDs from the postprocessed output for a W-2 form.
Config
{
/* output result of omit_fields in `postprocessorOutput` */
"postprocessor": {
"type": "jsonLogic",
"rule": {
"omit_fields": [
{
/* the source object, `"var": ""`, returns the current context, in this case, all extracted fields */
"var": ""
},
/* the IDs of the fields to omit */
[
"employers_id",
"employees_ssn"
]
]
}
},
"fields": [
{
"method": {
"id": "queryGroup",
"searchBySummarization": "page",
"queries": [
{
"id": "state",
"description": "state",
"type": "string"
},
{
"id": "state_wages",
"description": "state wages",
"type": "string"
},
{
"id": "state_tax",
"description": "state income tax",
"type": "string"
},
{
"id": "employers_id",
"description": "employers_id",
"type": "string"
},
{
"id": "employees_ssn",
"description": "employees_ssn",
"type": "string"
}
]
}
}
]
}Example document
The following image shows the example document used with this example config:
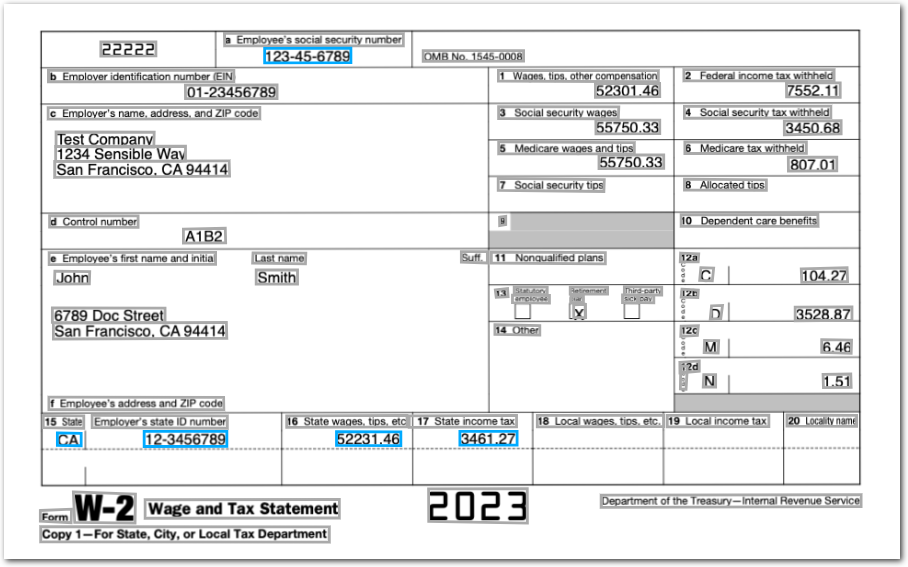
| Example document | Download link |
|---|
Postprocessor output
{
"state": {
"value": "CA",
"type": "string",
"confidenceSignal": "confident_answer"
},
"state_wages": {
"value": "52231.46",
"type": "string",
"confidenceSignal": "confident_answer"
},
"state_tax": {
"value": "3461.27",
"type": "string",
"confidenceSignal": "confident_answer"
}
}Extraction output
{
"state": {
"value": "CA",
"type": "string",
"confidenceSignal": "confident_answer"
},
"state_wages": {
"value": "52231.46",
"type": "string",
"confidenceSignal": "confident_answer"
},
"state_tax": {
"value": "3461.27",
"type": "string",
"confidenceSignal": "confident_answer"
},
"employers_id": {
"value": "12-3456789",
"type": "string",
"confidenceSignal": "confident_answer"
},
"employees_ssn": {
"value": "123-45-6789",
"type": "string",
"confidenceSignal": "confident_answer"
}
}Pick fields
Returns the specified fields. Takes an array of two items:
- an object to get fields from
- an array of field IDs to pick
{
"pick_fields": [
sourceObject,
["field_id_1", "field_id_2", "field_id_3"]
]
}The Pick Fields operator returns an empty object if:
- you pass an empty array as the second argument, or if Sensible can't find the specified field IDs
- the source object is empty, null, or undefined
Examples
Example 1
As a simplified example, given the following extracted fields:
{
"field_morning": "good morning",
"field_afternoon": "good afternoon",
"field_evening": "good evening"
}if you apply the rule:
{
"pick_fields": [
// `"var": ""` returns the current context, in this case, the preceding extracted fields
{ "var": "" },
// the IDs of the fields to be returned by the rule
["field_morning", "field_afternoon"]
]
}the rule outputs:
{
"field_morning": "good morning",
"field_afternoon": "good afternoon"
}Example 2
For a complete example, see Custom computation group.
Replace
Returns a modified string.
One of the following syntaxes:
{
"replace": {
"source": JsonLogic,
"find": /* string or JsonLogic that evaluates to string */
"replace": /* string or JsonLogic that evaluates to string */
}
}Or:
{
"replace": {
"source": JsonLogic,
"find_regex": regex,
"replace": /* string or JsonLogic that evaluates to string */
"flags": "i" /* optional */
}
}Where regex is a JavaScript-flavored regular expression. Double escape special regex characters, since the regex is in a JSON object (for example, \\s, not \s, to represent a whitespace character). This operation supports:
- regex capturing groups
- regex flags, such as
ifor case insensitive.
Examples
See Custom Computation.
Round
Rounds the specified numeric value. Takes as input the number to round and the number of decimal places to which to round.
{
"round": [/* number to round */, /* number of decimal places to round to */]
}For example:
{
"fields": [],
"postprocessor": {
"type": "jsonLogic",
"rule": {
"round": [5.32914, 2]
}
}
}
returns:
5.33Slice
Selects elements in an array from a starting index up to but not including an ending index. Returns the new array containing the selected elements.
"slice": [
[ /* array_to_slice */ ],
/* start_slice_index */,
/* end_slice_index */
]For example:
"slice": [
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
/* start from 1st element, stop before 2nd-to-last element */
0,
-2
]returns:
[
0,
1,
2
]Sort By
Sorts an array of objects by the specified key. The key's values must all be of the same type, either strings or numbers. Sorts in ascending alphanumeric order.
"sort_by":
[
[ /* array_of_objects_to_sort */ ],
"key_to_sort_by",
]For example, the following code sorts an array of dates:
{
"fields": [],
"postprocessor": {
"type": "jsonLogic",
"rule": {
"sort_by": [
{
/*
The array of objects to sort.
In practice, you often input an
array with `{"var":"field_key"}` syntax.
This example uses `preserve` to input an
array constant
as literal JSON rather than JsonLogic
*/
"preserve": [
{
"date": {
"source": "01/25/2024",
"value": "2024-01-25T00:00:00.000Z",
"type": "date"
},
"hours": {
"source": "7.41",
"value": 7.41,
"type": "number"
}
},
{
"date": {
"source": "01/27/2022",
"value": "2022-01-27T00:00:00.000Z",
"type": "date"
},
"hours": null
},
{
"date": {
"source": "01/28/2023",
"value": "2023-01-28T00:00:00.000Z",
"type": "date"
},
"hours": {
"source": "2.00",
"value": 2,
"type": "number"
}
}
]
},
// Sort by the date field's value
{ "var": "date.value" }
]
}
}
}
The preceding code sample returns the following output:
[
{
"date": {
"source": "01/27/2022",
"value": "2022-01-27T00:00:00.000Z",
"type": "date"
},
"hours": null
},
{
"date": {
"source": "01/28/2023",
"value": "2023-01-28T00:00:00.000Z",
"type": "date"
},
"hours": {
"source": "2.00",
"value": 2,
"type": "number"
}
},
{
"date": {
"source": "01/25/2024",
"value": "2024-01-25T00:00:00.000Z",
"type": "date"
},
"hours": {
"source": "7.41",
"value": 7.41,
"type": "number"
}
}
]Stateful Map
This operator maps an array and persists a state variable across items in the array.
Example use cases include:
-
Keeping a rolling balance of transactions.
-
Mixed headers and items data in a table: persist the headers and apply them to items until the header changes. For example, use the Stateful Map operation to keep track of the header rows (vendors) and data rows (paint names) in the following table:
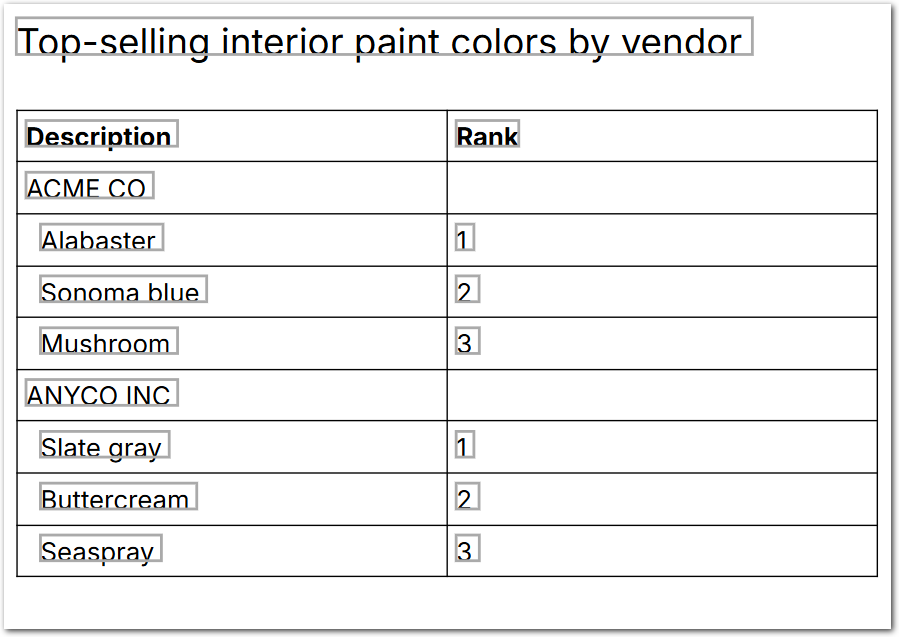
{
"stateful_map": [
[ /* 1st arg: array_to_map */ ],
{
/* 2nd arg: mapping function that has access to:
- `current` variable - the current item in the array
- `index` variable - index of current item in the array
- `state` variable - the current state
The function is expected to output an array with 2 elements:
[ <item or items to be added to the mapped array>, <updated state to use when mapping next item> ]
*/
},
{
/* 3rd arg (optional): initialize the state for 1st item in array.
If unspecified, state is undefined until set on 2nd iteration through loop
*/
}
]
}
Examples
The following example shows using the Stateful Map and Merge Objects operations to transform an extracted table into a list of rows. The table contains a mix of header and data rows, and the JsonLogic operation transforms the table by skipping header rows and appending header information to each row.
{
"fields": [
{
/* Step 1: Extract a fixed table starting at row 1 with 2 columns
Each column is defined with an id and index, and optionally a type */
"id": "raw_table_contents",
"anchor": "paint",
"method": {
"id": "fixedTable",
"columnCount": 2,
"startOnRow": 1,
"columns": [
{
"id": "description",
"index": 0
},
{
"id": "rank",
"index": 1,
"type": "number"
},
]
}
},
{
/* Step 2: Convert the table from column-wise format into an array of row objects */
"id": "raw_ranked_paints",
"method": {
"id": "zip",
"source_ids": [
"raw_table_contents"
]
}
},
{
/* The stateful_map operation is used to track which header we’re currently in.
If a row has rank: null, it's a header row, and its description becomes the new state.
If a row has a rank value, it's a data row, and the current state (i.e., the last header) is used to set the vendor
The result is a flat list of rows, each annotated with the appropriate vendor taken from the most recent header. */
"id": "ranked_paints",
"method": {
"id": "customComputation",
"jsonLogic": {
"stateful_map": [
{
/* The input array to map over: each item is a row from the table */
"var": "raw_ranked_paints"
},
{
/* the stateful mapping function
It has access to:
- the `current` item in the array,
- the `index` of the current item in the array
- a `state` variable
Sensible expects the mapping function to return [mapped item or items, updated state] */
"if": [
{
"==": [
/* Check if 'rank' cell is null to identify a header row */
{
"var": "current.rank"
},
null
]
},
/* If it's a header row:
- add nothing (empty array) to the mapped items
- Update the state to the current vendor (e.g. "ACME CO") */
[
[], /* adds no output to the mapped items */
{
/* new state = this row’s description */
"var": "current.description"
}
],
/* If it's a data row:
- Add the current row to the mapped items, merging in a field `vendor` field from state
- Retain the current state */
[
/* add current row to mapped items */
{
/* To the current row, merge in a new field 'vendor' from state */
"merge_objects": [
{
"var": "current"
},
{
/* create a new field with key 'vendor' and value from state */
"eachKey": {
"vendor": {
"var": "state"
}
}
}
]
},
{
/* Retain current state (the last header) */
"var": "state"
}
]
]
}
]
}
}
}
],
"computed_fields": [
{
/* Suppress intermediate outputs so they don't appear in the final result */
"id": "suppressOutput",
"method": {
"id": "suppressOutput",
"source_ids": [
"raw_table_contents",
"raw_ranked_paints"
]
}
}
]
}Example document
The following image shows the example document used with this example config:

| Example document | Download link |
|---|
Output
{
"ranked_paints": [
{
"description": {
"value": "Alabaster",
"type": "string"
},
"rank": {
"source": "1",
"value": 1,
"type": "number"
},
"vendor": {
"value": "ACME CO",
"type": "string"
}
},
{
"description": {
"value": "Sonoma blue",
"type": "string"
},
"rank": {
"source": "2",
"value": 2,
"type": "number"
},
"vendor": {
"value": "ACME CO",
"type": "string"
}
},
{
"description": {
"value": "Mushroom",
"type": "string"
},
"rank": {
"source": "3",
"value": 3,
"type": "number"
},
"vendor": {
"value": "ACME CO",
"type": "string"
}
},
{
"description": {
"value": "Slate gray",
"type": "string"
},
"rank": {
"source": "1",
"value": 1,
"type": "number"
},
"vendor": {
"value": "ANYCO INC",
"type": "string"
}
},
{
"description": {
"value": "Buttercream",
"type": "string"
},
"rank": {
"source": "2",
"value": 2,
"type": "number"
},
"vendor": {
"value": "ANYCO INC",
"type": "string"
}
},
{
"description": {
"value": "Seaspray",
"type": "string"
},
"rank": {
"source": "3",
"value": 3,
"type": "number"
},
"vendor": {
"value": "ANYCO INC",
"type": "string"
}
}
]
}Updated 3 months ago