Document range
Extracts consecutive lines succeeding the anchor line, for example, paragraphs of legal text. For the full definition of "succeeding", see Line sorting.
The Document Range method extracts all the text between an upper and a lower bound. To extract text from columns, use this method in combination with the Multicolumn preprocessor, or use the Paragraph method as an alternative.
You can use this method to return the coordinates of regions containing images.
Parameters
Note: For additional parameters available for this method, see Global parameters for methods. The following table shows parameters most relevant to or specific to this method.
| key | value | description |
|---|---|---|
| id (required) | documentRange | Optionally set "type": "paragraph" in the Field object to include newlines (\n) in the output. |
| stop | Match object or array of Match objects. default: none | Stops extraction at the top boundary of the matched line. The matched line isn't included in the method output. If this parameter and the Num Lines parameter are unspecified, matches to the end of the document. |
| numLines | integer. | Alternative to the Stop parameter. Extracts the specified number of lines succeeding the anchor. |
| includeAnchor | boolean. default: false | Includes the anchor line in the method output. If true, included in the total line count for the Num Lines parameter. |
| includeImages | boolean. default: false | Returns the zero-indexed page number and coordinates of regions containing images in the document range . Notes: If you set true, also set"type": "images" in the field object (see Examples section for an example). Returns image region coordinates, not image bytes or text lines. To extract structured data from images, see the Query Group method and configure the Multimodal Engine parameter. |
| offsetY | number in inches. | Specifies the number of inches to offset the start of the document range from the top boundary of the anchor line. Positive values offset down the page, negative values offset up the page. If the offset falls below all lines on the page containing the anchor, the offset starts at the top boundary of the first line on the next page that contains lines. For an example, see the Examples section. |
| stopOffsetY | number in inches. | Specifies the number of inches to offset the end of the document range from the top boundary of the stop line. Positive values offset down the page, negative values offset up the page. If the offset falls below all lines on the page containing the anchor, the offset starts at the top boundary of the first line on the next page that contains lines. |
Examples
Paragraphs and lists
The following example extracts a list of four sworn statements from a W-9 form.
Config
{
"fields": [
{
"id": "certification",
"anchor": "perjury",
"type": "paragraph",
"method": {
"id": "documentRange",
"stop": {
"type": "startsWith",
"text": "Certification instructions",
"isCaseSensitive": true
}
}
}
]
}Example document
The following image shows the example document used with this example config:

| Example document | Download link |
|---|
Output
{
"certification": {
"type": "string",
"value": "1. The number shown on this form is my correct taxpayer identification number (or I am waiting for a number to be issued to me); and 2. I am not subject to backup withholding because: (a) I am exempt from backup withholding, or (b) I have not been notified by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) that I am subject to backup withholding as a result of a failure to report all interest or dividends, or (c) the IRS has notified me that I am no longer subject to backup withholding; and\n3. I am a U.S. citizen or other U.S. person (defined below); and\n4. The FATCA code(s) entered on this form (if any) indicating that I am exempt from FATCA reporting is correct."
}
}Images
The following example shows extracting two images' coordinates.
Config
{
"fields": [
{
"id": "python_icons",
"type": "images",
"anchor": "icons",
"method": {
"id": "documentRange",
"includeImages": true,
"stop": {
"type": "startsWith",
"text": "React",
"isCaseSensitive": true
}
}
},
]
}Example document
The following image shows the example document used with this example config:
| Example document | Download link |
|---|
Output
{
"python_icons": {
"images": [
{
"page": 0,
"boundingPolygon": [
{
"x": 1.021,
"y": 2.208
},
{
"x": 3.156,
"y": 2.208
},
{
"x": 3.156,
"y": 4.333
},
{
"x": 1.021,
"y": 4.333
}
]
},
{
"page": 0,
"boundingPolygon": [
{
"x": 1.021,
"y": 4.844
},
{
"x": 2.771,
"y": 4.844
},
{
"x": 2.771,
"y": 6.573
},
{
"x": 1.021,
"y": 6.573
}
]
}
]
}
}Offset Y parameter
Config
The following example shows using an Offset Y parameter to extract content that precedes the anchor. This example also shows:
- using the Document Range as an alternative to the Row method to extract multiline rows.
- using the Type Filter parameter to remove unwanted matched lines, in this example, the claims dates.
{
"fields": [
{
"id": "injuries",
"type": "sections",
"range": {
"anchor": {
"match": {
"type": "includes",
"text": "claim number"
}
}
},
"fields": [
{
"id": "injury_multiline",
"method": {
"id": "documentRange",
"stop": {
"text": "Claim date",
"type": "startsWith"
},
"offsetY": -0.3,
"typeFilters": [
"date"
]
},
"anchor": {
"match": {
"type": "startsWith",
"text": "Injury"
}
}
}
]
}
]
}Example document
The following image shows the example document used with this example config:
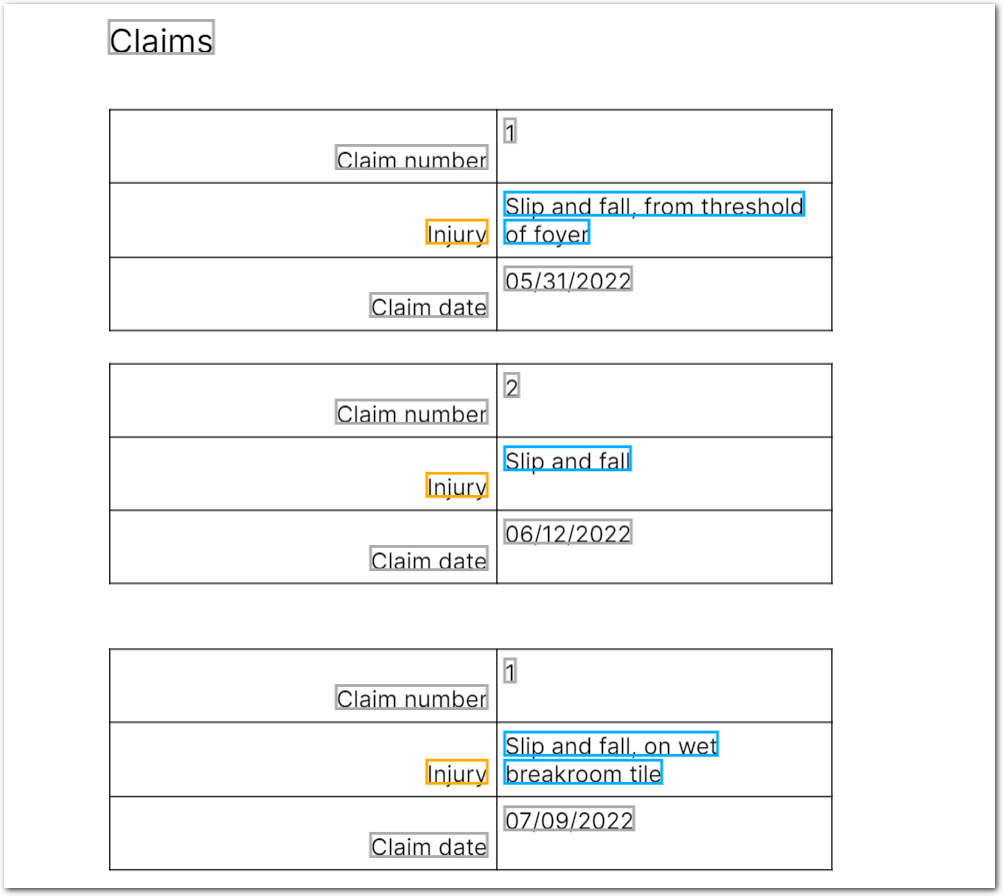
| Example document | Download link |
|---|
Output
{
"injuries": [
{
"injury_multiline": {
"type": "string",
"value": "Slip and fall, from threshold of foyer"
}
},
{
"injury_multiline": {
"type": "string",
"value": "Slip and fall"
}
},
{
"injury_multiline": {
"type": "string",
"value": "Slip and fall, on wet breakroom tile"
}
}
]
}Notes
Extracting images
The Document Range supports extracting non-text images that you can then render. For example, extract photos of buildings embedded in an inspection report and save them to a backend. It doesn't support extracting structured data from the images.
Note: To extract structured data from an image, use the Query Group method with the Multimodal Engine parameter configured. For example, extract facts about the building, such as whether it's multistory-story or single-story.
To extract images, set "includeImages":true for the Document Range method. Sensible returns the image region coordinates rather than the actual encoded bytes of images. If you want to extract the images themselves, you can use a PDF library in your chosen programming language to follow these general steps:
- Render the page containing the image to a bitmap. Page numbers are zero-indexed in the Sensible output.
- Convert Sensible's coordinates for the image region to pixel per inch (PPI) coordinates. Sensible's region coordinates follow these conventions:
- they're in reference to a 0.0 origin at the top left corner of the page (not the bottom left origin, as is for example the convention with the popular PDF.js library)
- they're in inches (to convert inches to pixels, multiply the inches coordinates by your PPI setting. For example, an x-coordinate of 3.156 inches is ~227 pixels for a PPI setting of 72 (72 PPI * 3.156 inches)).
- they're ordered clockwise from top left: (top left), (top right), (bottom right), (bottom left)
- Extract a partial bitmap defined by the PPI coordinates of the image from the rendered page.
- Encode the bitmap to bytes in the image format of your choice.
Updated 3 months ago