NLP table
Extracts a table based on your natural-language description of the data you want to extract. This method can extract tables that span multiple pages. This method is suited to tables that have a header row, where each row is a data element. Not suited to tables where the header is in the first column and the columns are data elements, or to other complex table layouts. For alternatives to this method, see Table methods.
Prompt Tips
-
Extract all columns to get the best results. If you describe only a few of the columns, your results may be less accurate.
-
Use the table titles or table column headers in the document as descriptions.
-
For more information about how to write descriptions, or "prompts", see Query Group.
-
For advanced options, see Advanced LLM prompt configuration.
For information about how this method works, see Notes.
Parameters
Note You can configure some of the following parameters in both the NLP preprocessor and in a field's method. If you configure both, the field's parameter overrides the NLP preprocessor's parameter.
| key | value | description | interactions |
|---|---|---|---|
| id (required) | nlpTable | ||
| description | string | A prompt that describes the table's subject matter as a whole. As part of finding the best-matching table, Sensible compares the table title, if present, to this description. For more details about how Sensible uses the description, see the Notes section. | |
| columns (required) | array | An array of objects with the following parameters: - id (required): A user-friendly ID for the column in the extraction output. - description (required): A prompt that describes the data you want to extract from the column. This prompt can include instructions to reformat or filter the column's data. For example, provide prompts like " transaction amount. return the absolute value" or "vehicle make (not model)". - type: The table cell's type. For more information, see types. - isRequired (default false): If true, Sensible omits a row if its cell is empty in this column, or if the contents don't match the value you specify in this column's Type parameter. If false, Sensible returns nulls for empty cells in the row. Note that if you set this parameter to true for one column, Sensible omits the row for all columns, even if the row had content under other columns. | |
| TABLE RECOGNITION | |||
| rewriteTable | Boolean. default: true | If true, you can use the column descriptions to prompt the LLM to split or merge columns or otherwise restructure the table. Configure this to false to improve performance, to avoid LLM token overflow errors caused by tables that exceed 4,000 tokens, or to troubleshoot an incomplete table extraction. If false, Sensible returns the table body unchanged from the OCR extraction, and the only change you can make is to rename the column headings using the columns' ID parameters. | If you set this parameter to true, Sensible overrides the LLM Engine parameter. For more information, see the Notes section. |
| pageSpanThreshold | object | Configure the Page Span Threshold parameter to troubleshoot automatic multi-page table recognition. By default, Sensible detects multi-page tables by checking if the table is near the top or bottom of the page. If it is, Sensible searches previous and succeeding pages for continuations of the table. This default behavior fails when intervening, non-table text introduces a large vertical space between a multi-page table and the top or bottom of a page, bumping the table toward the center of the page. Examples of non-table text include footnotes and text box inserts. To allow for such large spaces, configure the following parameters: - top: number. default: 0.4. Sensible searches the previous page for a continuation of a multi-page table if the table starts in the top 40% of the page. Change the percent using this parameter.- bottom: number. default: 0.2. Sensible searches the next page for a continuation of a multi-page table if the table ends in the bottom 20% of the page. Change the percent using this parameter.Sensible continues merging the multi-page table until the Page Span Threshold conditions are no longer met, or until Sensible encounters LLM token limits. | |
| detectTableStructureOnly | boolean. default: false | Set this parameter to true to troubleshoot optional character recognition (OCR) in a table. If true, Sensible bypasses the text output by the table recognition OCR provider. Sensible instead recognizes the table's text using the OCR engine specified by your document type, or by using text embedded in the document file if present. For an example, see Example: Troubleshoot Table OCR. If "detectTableStructureOnly": true causes incorrect line sorting, set annotateSuperscriptAndSubscript": true to correct the line sorting. | |
| annotateSuperscriptAndSubscript | boolean. default: false | Set to true only if the Detect Table Structure Only parameter is set to true. When true: - Sensible annotates subscript and superscript text in the table with [^...] and [_...], respectively. This parameter doesn't support annotating text in multi-line cells. | |
| TROUBLESHOOT PROMPT | |||
| llmEngine | object | Configures the LLM model Sensible uses to extract data from the context. Configure this parameter to troubleshoot situations in which Sensible correctly identifies the part of the document that contains the answers to your prompts, but the LLM's answer contains problems. For example, Sensible returns an LLM error because the answer isn't properly formatted, or the LLM doesn't follow instructions in your prompt. Contains a provider parameter with the following options:- If set to open-ai (default), Sensible uses an OpenAI model.- If set to anthropic, Sensible uses an Anthropic model.- If set to google, Sensible uses a Google model.For more information about models, see LLM models. | |
| FIND CONTEXT | |||
| pageRange | object | Configures the possible page range for finding the context in the document. If specified, Sensible creates chunks in the page range and ignores other pages. For example, use this parameter to improve performance, or to avoid extracting unwanted data if your prompt has multiple candidate answers. Contains the following parameters: startPage: Zero-based index of the page at which Sensible starts creating chunks (inclusive). endPage: Zero-based index of the page at which Sensible stops creating chunks (exclusive). | Sensible ignores this parameter when searching for a field's anchor. If you want to exclude the field's anchor using a page range, use the Page Range preprocessor instead. |
| CONFIGURE CONTEXT SIZE | |||
| chunkCount | number. default: 5 | The number of top-scoring document chunks Sensible combines as context as part of the full prompt it submits to an LLM. |
Examples
The following example shows using the NLP Table method to extract information from tables about insured vehicles and insurance transactions.
Config
{
"fields": [
{
/* the id is a user-friendly name for the target table */
"id": "insured_vehicles_table",
"type": "table",
"method": {
"id": "nlpTable",
/* overall description of table's contents */
"description": "insured vehicles",
"columns": [
{
/* for each column, provide a user-friendly ID
and a description of the data you want to extract from the column
and optional instructions to filter or reformat the data*/
"id": "manufacturer",
"description": "vehicle make (not model)",
},
{
"id": "year",
"description": "year of manufacture",
}
]
}
},
{
"id": "transactions_table",
"type": "table",
"method": {
"id": "nlpTable",
"description": "transactions for insurance account",
"columns": [
{
"id": "transaction_date",
/* note LLMs have some limitations due to its training data.
For example, if an LLM doesn't know the current year
it makes one up in the output */
"description": "transaction date. If there's no year, append the current year.",
},
{
"id": "transaction_description",
"description": "transaction description"
},
{
"id": "amount",
"description": "transaction amount, returned as an absolute value",
"type": "currency"
}
]
}
}
],
"computed_fields": [
/* optional: for cleaner output, zip each table
into an array of rows objects */
{
"id": "zipped_insured_vehicles",
"method": {
"id": "zip",
"source_ids": [
"insured_vehicles_table",
]
}
},
{
"id": "zipped_transactions",
"method": {
"id": "zip",
"source_ids": [
"transactions_table",
]
}
}
]
}Example document
The following image shows the example document used with this example config:
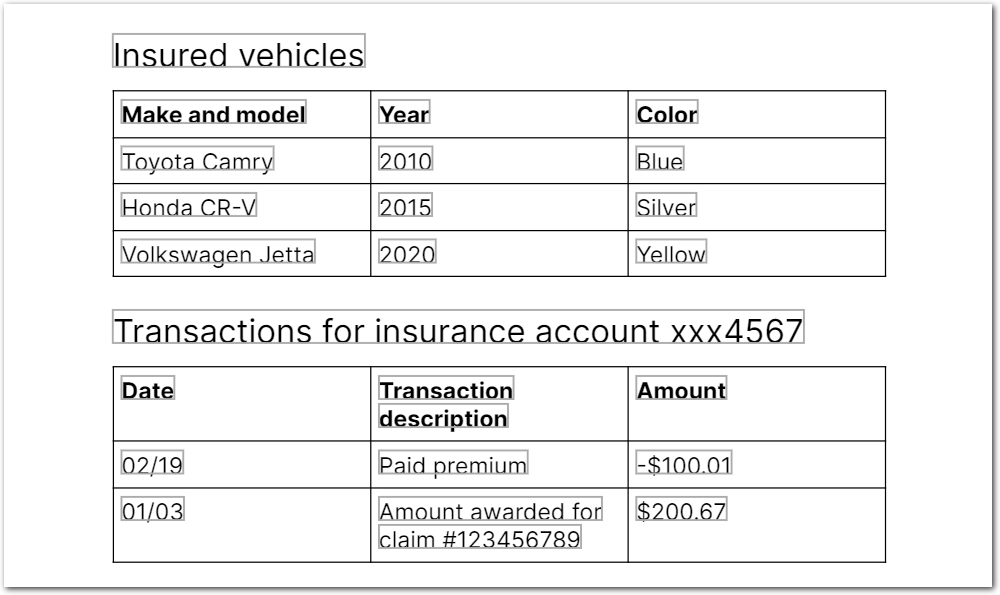
| Example document | Download link |
|---|
Output
{
"insured_vehicles_table": {
"columns": [
{
"id": "manufacturer",
"values": [
{
"value": "Toyota",
"type": "string"
},
{
"value": "Honda",
"type": "string"
},
{
"value": "Volkswagen",
"type": "string"
}
]
},
{
"id": "year",
"values": [
{
"value": "2010",
"type": "string"
},
{
"value": "2015",
"type": "string"
},
{
"value": "2020",
"type": "string"
}
]
}
],
"title": {
"type": "string",
"value": "Insured vehicles"
}
},
"transactions_table": {
"columns": [
{
"id": "transaction_date",
"values": [
{
"value": "02/19",
"type": "string"
},
{
"value": "01/03",
"type": "string"
}
]
},
{
"id": "transaction_description",
"values": [
{
"value": "Paid premium",
"type": "string"
},
{
"value": "Amount awarded for claim #123456789",
"type": "string"
}
]
},
{
"id": "amount",
"values": [
{
"source": "-$100.01",
"value": -100.01,
"unit": "$",
"type": "currency"
},
{
"source": "$200.67",
"value": 200.67,
"unit": "$",
"type": "currency"
}
]
}
],
"title": {
"type": "string",
"value": "Transactions for insurance account xxx4567"
}
},
"zipped_insured_vehicles": [
{
"manufacturer": {
"value": "Toyota",
"type": "string"
},
"year": {
"value": "2010",
"type": "string"
}
},
{
"manufacturer": {
"value": "Honda",
"type": "string"
},
"year": {
"value": "2015",
"type": "string"
}
},
{
"manufacturer": {
"value": "Volkswagen",
"type": "string"
},
"year": {
"value": "2020",
"type": "string"
}
}
],
"zipped_transactions": [
{
"transaction_date": {
"value": "02/19",
"type": "string"
},
"transaction_description": {
"value": "Paid premium",
"type": "string"
},
"amount": {
"source": "-$100.01",
"value": -100.01,
"unit": "$",
"type": "currency"
}
},
{
"transaction_date": {
"value": "01/03",
"type": "string"
},
"transaction_description": {
"value": "Amount awarded for claim #123456789",
"type": "string"
},
"amount": {
"source": "$200.67",
"value": 200.67,
"unit": "$",
"type": "currency"
}
}
]
}Notes
For an overview of how the NLP Table method works, see the following steps:
-
Sensible makes a list of the pages that are most likely to contain your target table. To make the list:
- Sensible concatenates all your column descriptions with your overall table description.
- Sensible splits the document into equal-sized chunks. A chunk is less than or equal to a page in length.
- Sensible scores your concatenated table descriptions against each chunk.
- Sensible gets a list of page numbers from the top-scoring chunks.
-
Sensible extracts all the tables on the pages most likely to contain your table, using the OCR engine specified by the document type. Sensible supports multi-page tables.
-
Sensible scores each table by how well it matches the descriptions you provide of the data you want to extract. To create the score:
-
Sensible concatenates all your column descriptions with your overall table description.
-
Sensible concatenates a number of the first rows of the table with the table title. Sensible uses the table title extracted by the table OCR provider, or falls back to using the text in a region above the table if the OCR provider doesn't find a title.
-
Sensible scores the two concatenations.
-
-
Sensible creates a full prompt for the LLM that includes the top-scoring table, page hinting data, and your prompts. For more information about the full prompt, see Advanced LLM prompt configuration.
- If
rewriteTable:false, the full prompt instructs the LLM (as specified by the LLM Engine parameter) to rewrite or restructure the best-scoring table based on your column descriptions and your overall table description. - If
rewriteTable: true, the full prompt instructs a nonconfigurable LLM to rewrite the column headings' IDs, but doesn't otherwise restructure the table.
- If
-
Sensible returns the restructured table.
Updated 3 months ago